Need to replace bulbs for your vehicle? How do you navigate the bulb market without missing out on the lighting needs, bulb type and size? Cars contain several bulbs, each serving a specific purpose. Whether you are shopping for a headlight, tail light, brake light, indicator bulbs or even interior bulbs, ensure it fits in the sockets.
Drivers have several options to choose from, ranging from standard halogen bulbs, LED bulbs and Xenon bulbs. The sizes of all these categories are available in standard bulb size charts. Bulbs have alphanumeric characters on them that indicate sizes. This guide provides vital information to help you choose the best set of bulbs for your priced vehicle.
What headlight bulb do I need?
Proper lighting is undebatable when driving in the dark. Headlight bulbs provide beam patterns that illuminate the road for superb night visibility. Most vehicles have standard halogen bulbs with double filaments. The filaments brighten when heated within the halogen environment. The double filaments allow adjustment between high beams and low beams. Alternatively, drivers can go for LED type or Xenon bulbs that offer better illumination. How do you go about choosing headlight bulbs?
Bulb selection may seem like a straightforward activity. In reality, finding the perfect fit means evaluating the design of the fitting and the size of the bulb while ensuring it offers a suitable beam pattern. You may end up purchasing the exact halogen-type bulb size but fail to check if it is a single or double filament bulb. It means you end up driving on a low beam, which could impact driving safety at night. When upgrading to LED or Xenon lights, you may have to modify bulb fittings for perfect seating on the sockets.
Fitting information of bulbs is available at the base of their casings. Vehicle manufacturers provide this information in manuals. If you are having difficulty identifying the correct type of headlight bulb using the online bulb selection tool, consult a professional or bulb dealer.
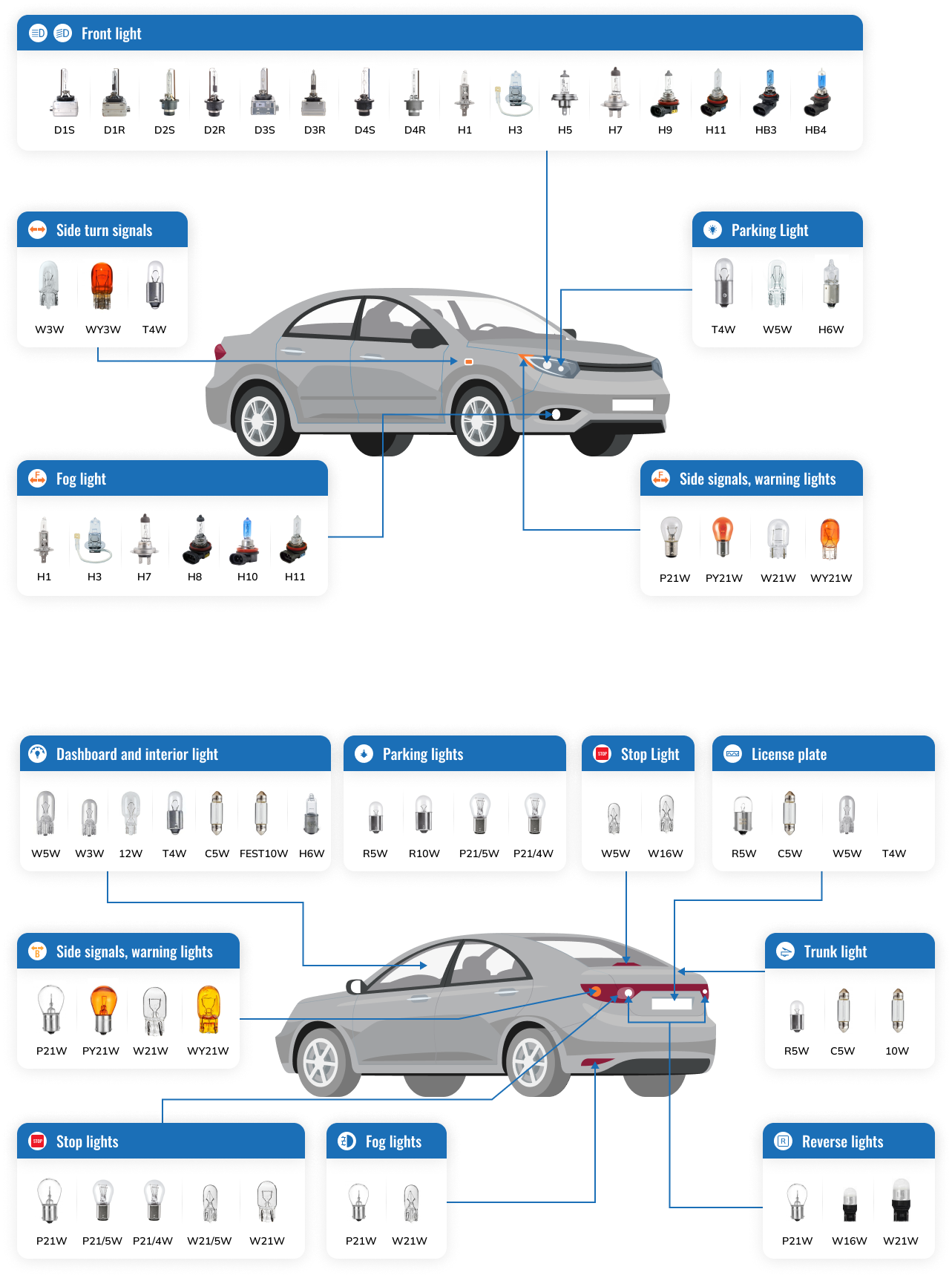
Automotive bulb types by position
Automotive bulbs are available at the front, rear, sides and interiors of the car. The automotive battery powers all these bulbs. Aside from choosing the correct bulb size for interior or exterior lighting, the bulb must be compatible with the electronic configuration of the vehicle. Given the advancements in automotive technology, bulb incompatibilities may cause errors that affect standard operations of the electronic control units. Irrespective of their positions, drivers must exercise caution when removing or replacing bulbs. The lighting intensities for each bulb type are specific to its application. Headlights provide superior illumination to fog lights. Drivers may opt for lighting modifications to enhance aesthetics and match driving needs.
Exterior lights
Forward lighting includes headlights (high and low beams) and fog light bulbs. Turn signal bulbs (indicators) are available at the front and rear sides of the vehicle. All vehicles have reverse and brake light bulbs at the rear. License plate light bulbs also form part of exterior lighting. Each of these bulbs is crucial for road safety.
Off-road enthusiasts fit grille lights, pods lights and light bars which provide additional illumination in dark and bushy roads. These bulbs bear unique designs and adaptations for ultimate performance under different driving conditions.
Interior lights
Interior lights are not just limited to visibility. Drivers customize these lights to enhance interior aesthetics using unique, multi-color or low-light bulbs. Interior lights are less energy-intensive in comparison with their exterior counterparts. Typical interior lights include door lights that enhance the visibility of door handles and controls. There are also sets of dome lights that brighten when doors open. You can install dome lights at the front and the rear sides of your vehicle.
Other interior lights include accent lights, map lights and trunk lights. Trunk lights are particularly critical for drivers who frequently load or unload goods in the dark. There are no limits to color combinations for interior light bulbs as long as they do not impede your driving capabilities and attention.
How to decode car bulb numbers
The base of automotive light bulbs contains figures such as H11. Manufacturers assign these numbers on bulbs to indicate compliance with international regulations. A bulb having H11 is usable for automotive lighting without any general restrictions. They use a 12V or 24 V power supply and can provide luminous flux up to 1,350 lm.
Types of Automotive Bulbs
Automotive bulbs come in different shapes and sizes. Bulbs are currently differentiated by their type and features. The three common types of automotive bulbs include halogen, Xenon HID, and LED.
These are further differentiated according to their performance, style, and durability. In this article, we’ll cover the main differences between automotive bulbs and help you decide what to choose when shopping.
Car light bulb types by technology
Average drivers struggle with the numerous technical jargon around bulbs. Why would the prices of bulbs having similar sizes vary? Why would some bulbs last longer than others? Manufacturers use diverse bulb technologies to differentiate the performances of bulbs. That explains why some bulbs are brighter than others and why beam consistencies vary. Below is a description of bulb technologies.
Halogen Bulbs
Halogen bulbs were invented in early 1960s. They became mainstream in American in the 1980s. They took over from electric composite headlights which had been in use in America for more than four decades.
Halogen headlights are still in use today. They feature a tungsten filament contained in a glass casement filled with halogen gas. Current is passes through the filament causing it to glow. This then produces the light we need when driving at night.
The halogen gas helps to maintain the filament in good working condition and prevents the bulb from darkening. It is necessary for the longevity of the bulb. Some of the advantages of having halogen bulbs is that they are cheaper than other modern alternatives.
They are also easier to replace in case they burn out. Cars use them for both interior and exterior lighting. Unfortunately, they are not as durable or as long-lasting as their modern counterparts.
For this reason, car manufacturers are fitting them in fewer cars than before. They are slowly being phased out with the continuous advancement in technology.
Halogen bulbs have been available for a very long time. The bulbs contain resistive filaments that heat up when current flows through them. As the filament heats up, it brightens and lights up the surrounding. Manufacturers fill the bulbs with halogen gas that prevents discoloration. The extreme heat of the filament turns the bulb black and lowers its brightness with time. Halogen-type valves emit a yellowish light.
Pros
- Cheaper than other bulb types
- Easy to replace
- Versatile (usable for interior and exterior lighting needs)
Cons
- Less bright than other bulb types
- Prone to burn-outs which lowers their durability.
LED
LED bulbs are what most car manufacturers choose to fit in vehicles today. They use light emitting diodes to produce light. Current is passed through semiconductors which turn it into light without using much energy.
LED bulbs were first used as interior lights in cars. Today, they make up the majority of the exterior lights that vehicles have. They are becoming more popular due to their ability to produce more white light while conserving energy.
In addition, their small size allows car manufacturers to play around with different vehicle designs. They are able to blend in with the curves and design patterns of many vehicles. Most of them allow for the use of high beams, low beams, and turn signals in one headlight.
LED bulbs also last way longer than halogen and HID bulbs. Once put on a car, they do not need to be replaced for a very long time. If you’re considering upgrading to LED headlights, ensure that what you choose is road legal.
These advanced, energy-saving automotive bulbs use light-emitting diodes. The flow of voltage through the semi-conductors (diodes) changes into light. This technology is finding its way into the manufacture of interior and exterior lighting bulbs. LED bulbs provide bright white light and a more intensive beam.
Unlike halogen bulbs, there are restrictions for using LED bulbs for forward lighting. The semi-conductors consume little power making them low-temperature bulbs. It enhances their longevity.
Pros
- Excellent energy efficiency
- Better brightness than halogen bulbs
- More durable
Cons
- More expensive
- Restricted road usage
HID
Xenon or HID bulbs are a popular alternative to halogen bulbs. They are brighter and more energy efficient. Rather than using a filament to produce light, these types of automotive bulbs use an electric arc positioned between two electrons inside a glass casement.
The casement is filled with xenon gas which helps to produce a much brighter and whiter light than halogen bulbs. Many car owners prefer to switch to HID or xenon bulbs because they last longer and produce more light.
However, it’s good to note that they are not ideal for interior lighting. Xenon bulbs can also be quite expensive and are sometimes too bright to be street legal. If you’re looking to replace your halogen bulbs with xenon, ensure that what you pick is allowed in your state
High-intensity discharge (HID) bulbs provide better brightness than halogen-type bulbs. These automotive bulbs use Xenon gas that gives off a whitish glow. The bulbs have a pair of electrodes within a glass tube. The power supply from the battery creates an electric arc between the electrodes. As Xenon gas discharges into the glass tubes, it glows. Unlike LED and halogen-type bulbs, they require an external control mechanism. These bulbs come with an electric control module that initiates and controls lighting. They are brighter than halogen bulbs and are suitable for headlights.
Pros
- Brighter than traditional halogen bulbs
- Last longer
Cons
- Costlier than halogen bulbs
Projector Vs reflector headlights
What kind of lighting do you need for night driving? The intensity and coverage of the light beam will depend on the design of the bulb housing. Manufacturers adopt two technologies:
- Projector headlights
- Reflector headlight
Reflector headlights use bowl-shaped casings made from steel. The bowl contains reflective mirrors which redirect the light to the road. The mirroring surface is chrome-painted. These headlights have well-designed lenses at the front that define the shape and width of the beam on the road. Although this technology has been in existence for a long time, it remains a preferable choice among headlight manufacturers. They are simple to manufacture and often occupy less space.
The mirror allows the reflectors to cover a wider angle. However, the intensity of the light beam is smaller.
Projector headlights are a modern innovation that seeks to minimize light waste. They use similar technologies to reflector headlights. The bulb is enclosed in a reflective, bowl-shaped casing. The headlight has a powerful lens that intensifies the brightness of the beam. To enhance the focus of the light beam on the road surface, manufacturers use an angular cut-off shield. It directs the light into a smaller region, emitting a bright light. Projector technology enhances road safety as it is less likely to blind oncoming drivers.
Using our headlight bulb finder
Search by Year, Make and Model, and Position
Utilize our advanced Bulb Finder tool to scrape through a database of bulbs and find the best replacement part for your vehicle. Select the vehicle’s model, make and year of manufacture, and position from the drop-down menu below. We have a comprehensive database for different cars, vans, and trucks.
Aftermarket light bulb replacement guide
Once in a while, you have to replace your bulbs. There are always two options on the table, choosing a standard OEM (original equipment manufacturer) part or upgrading to an aftermarket bulb. Aftermarket bulb manufacturers focus on better lighting and durability. Although aftermarket bulbs offer superior performance, it is easy to err in the selection process. How can you avoid this?
- Understand the types of automotive bulbs available in the market.
- Refer to the owner’s manual or refer to the previous bulb for technical specifications.
- Check if the aftermarket bulb is compatible with the socket and electronic systems of the vehicle.
- Utilize our online bulb finder to filter available alternatives.
- If you are still stuck, consult our experts.
Single Beam VS Dual Beam
A single beam automotive headlight uses two bulbs. The first produces a low beam while the other, a high beam. Each of these bulbs has a single filament. It is the bulbs that determine whether the headlight is single or dual-beam.
Drivers can confuse dual beams for headlights using a pair of bulbs. On the contrary, dual-beam headlights use one bulb which has two filaments. The filaments emit two lights that differ in intensity. It is inadvisable to use a dual beam bulb in the place of a single beam bulb as headlight operating mechanisms differ.
Low Beam VS High Beam
Beam angles affect visibility ranges.
A high beam is usually straight or takes an upward orientation. It is intense and covers longer distances. High beams are suitable for driving in poorly lit zones and should only be active for a short time.
Low beams are oriented downwards on the road. The low beam covers short distances and is essential for driving on busy streets. It is the default, low-light setting for automotive headlights. Their low illumination intensities prevent the blinding of oncoming drivers.
Performance
If you’re looking for the brightest lights, maximum performance bulbs provide the most amount of light possible and allow drivers to see way farther down the road. They are a great improvement from standard bulbs.
It’s important to note that they can sometimes be more expensive. Their intense light also tends to shorten their lifespan. Ensure that what you choose lasts as long as you need and that it provides value for your money.
Style
Manufacturers also provide styling bulbs designed to give your car a unique look. They feature cool color temperatures and produce different colors. The most popular colors are blue and white.
However, these may not always be legal. Those that produce too much white light can dazzle other motorists. Those that produce a different color other than white can also lower visibility. Always check your state laws before buying styling bulbs.
Durability
Lastly, long-lasting and eco-friendly bulbs are a great alternative for anyone looking to save some money. These are made to serve longer than normal without burning out or requiring a replacement. They also consume less power. They are a great option if you’re on a budget.
Conclusion
As seen above, there’s something for everyone when it comes to choosing automotive bulbs for your car. When shopping, confirm that the bulb you want is legal and that it is ideal for your vehicle.
